To configure Docker for managing clusters in Nirmata, start by creating the certificates. After creating the certificates, update the Log Settings.
Create Certificates for Configuring Docker for Managed Clusters
- Create a directory at
/etc/docker/certs.d - Ensure that sure all certificates are created using the hostname.
- Run the Create Key Command to generate the key
- Run the Create Certificates Command to generate the certificates
Create Key Command:
openssl genrsa -out client.key 4096
Create Certificates Command:
openssl req -new -x509 -text -key client.key -out client.cert
Store certificates in the following directories:
/etc/docker/certs.d/ <-- Certificate directory
└── localhost:5000 <-- Hostname:port
├── client.cert <-- Client certificate
├── client.key <-- Client key
└── ca.crt <-- Certificate authority that signed the cert
Update Log Settings
Invoke log rotation to avoid encountering disk space issues using the Log Rotation Command.
Log Rotation Command:
vi /etc/docker/daemon.json
Next, add the following lines to the daemon.json:
NOTE: edit these lines according to the internal production policies.
{
"log-driver": "json-file",
"log-opts": {
"max-size": "25m",
"max-file": "5"
}
}
Locate the docker /var/lib/docker folder. The location of this folder is operating system dependent.
Mounting the Cluster Elsewhere
To mount the cluster somewhere else, update the sysconfig/docker file and daemon.json file.
Update sysconfig/docker File
Update the sysconfig/docker file as shown:
cat /etc/sysconfig/docker
OPTIONS='--selinux-enabled --log-driver=journald --signature-verification=false -D -g /where/you/want/docker'
g -> specify docker's root directory
Update the daemon.json File
Update the daemon.json file as shown:
[root@docker-host-1 ~]# cat /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"graph": "/where/you/want/docker"
}
[root@docker-host-1 ~]#
Stop and Restart Docker Service
Before restarting the Docker service, complete configuration steps for running Docker hosts.
Stop the Docker service using the Stop Docker Command.
Stop Docker Command:
[root@docker-host-1 ~]# systemctl stop docker
Move existing Docker’s root directory (/var/lib/docker/) content to new directory (/where/you/want/docker) using the Move Root Directory Command.
Move Root Directory Command:
[root@docker-host-1 ~]# mv /var/lib/docker/* /where/you/want/docker
[root@docker-host-1 ~]#
[root@docker-host-1 ~]# ls -lrt /var/lib/docker
total 0
[root@docker-host-1 ~]# ls -lrt /where/you/want/docker
total 4
drwx--x--x. 3 root root 20 Feb 18 14:21 containerd
drwx------. 4 root root 32 Feb 18 14:21 plugins
drwx------. 3 root root 22 Feb 18 14:21 image
drwx------. 2 root root 6 Feb 18 14:21 trust
drwxr-x---. 3 root root 19 Feb 18 14:21 network
drwx------. 2 root root 6 Feb 18 14:21 swarm
drwx------. 2 root root 24 Feb 18 14:21 builder
drwx------. 4 root root 169 Feb 21 08:43 volumes
drwx------. 5 root root 222 Mar 3 12:39 containers
drwx------. 2 root root 6 May 3 07:57 tmp
drwx------. 2 root root 6 May 3 07:57 runtimes
drwx------. 40 root root 4096 May 3 07:57 overlay2
Restart Docker service using the Restart Docker Command.
Restart Docker Command:
[root@docker-host-1 ~]# systemctl restart docker
[root@docker-host-1 ~]#
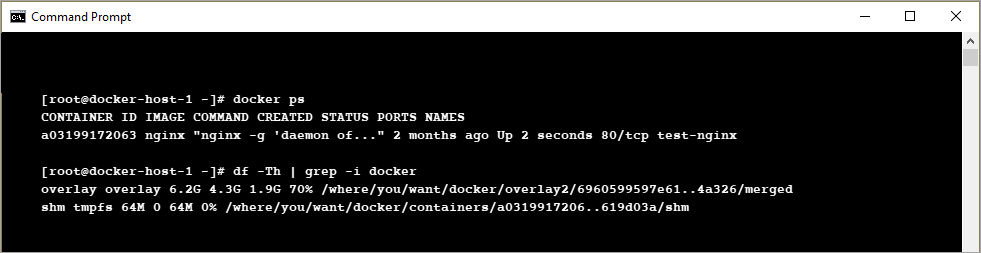
Start any one of the containers and check Docker’s root directory using the Check Root Directory Command.
Check Root Directory Command:
[root@docker-host-1 ~]# docker start containerID
The result should be similar to this: